Aug 04, 2025
Introduction
A centrifugal pump is a mechanical device that converts the rotational energy of an impeller into fluid kinetic energy to transport liquids. Centrifugal pumps are widely used in industries such as water treatment, oil and gas, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, and are key equipment for efficient liquid transportation. In this article, we will explore the working principle of centrifugal pumps, their key components, different types, and applications to help you gain a comprehensive understanding of what centrifugal pumps are. Continue reading to learn more!
How Does a Centrifugal Pump Work?
The working principle of a centrifugal pump involves an electric motor driving the impeller to rotate at high speed, thereby causing the liquid inside the pump to form a rotating flow and generating high kinetic energy at the impeller outlet. Under the influence of centrifugal force, the liquid flows along the pump casing toward the outlet or is transported to the next stage impeller. Simultaneously, a low-pressure zone forms at the center of the impeller due to the outflow of liquid, creating a pressure difference with the liquid at the suction inlet, which drives the liquid to continuously enter the pump body. As the impeller continues to rotate, the pump achieves continuous suction and discharge, completing the liquid transportation process.
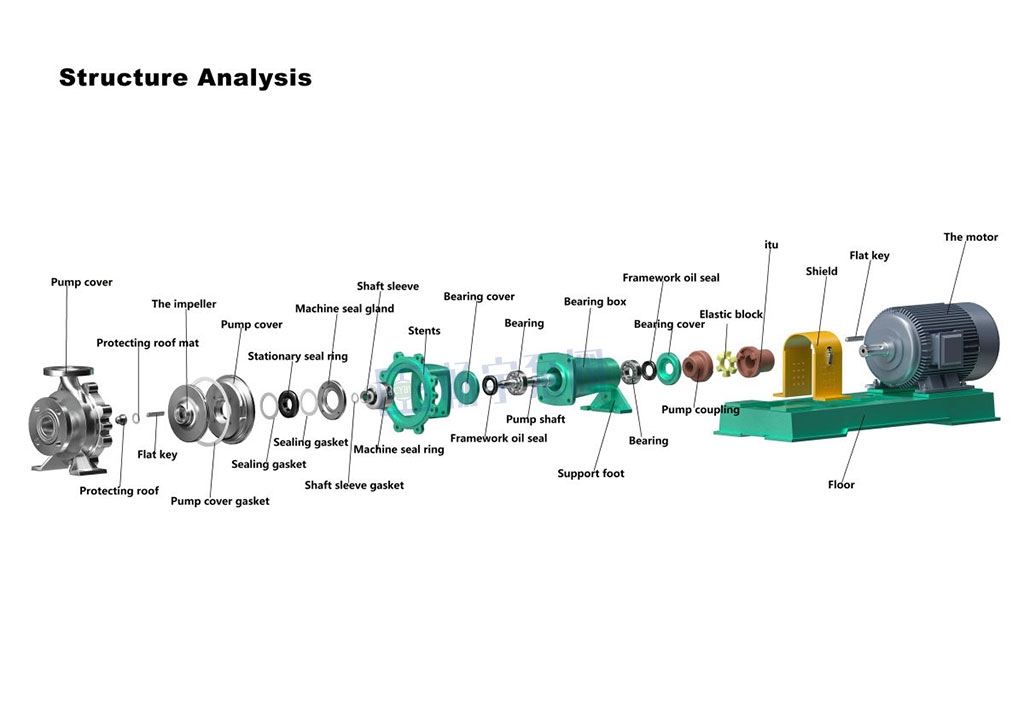
Centrifugal Pumps Parts
The centrifugal pump parts mainly consist of impellers, pump casings, pump shafts, bearing assemblies, sealing devices, suction and discharge ports, and drive motors. The following are the functional characteristics of each component:
Impeller: The impeller is the rotating element that imparts kinetic energy to the fluid, generating centrifugal force to move the liquid outward.
Pump Casing: The casing encloses the impeller and directs the flow of liquid from the impeller to the discharge outlet while converting velocity into pressure.
Shaft: The shaft transmits mechanical energy from the motor to the impeller, maintaining stable rotation and alignment.
Bearing Assembly: Bearings support the shaft and reduce friction, making is smooth and precise operation.
Mechanical Seal or Packing: Prevent liquid from leaking along the shaft where it exits the casing.
Suction and Discharge Nozzles: The suction nozzle allows fluid to enter the pump, while the discharge nozzle guides it out under pressure.
Motor or Driver: The motor provides the necessary power to rotate the impeller and drive the pumping process.
Types of Centrifugal Pumps
industrial centrifugal pumps have a variety of designs and models to meet different industrial application needs. The following are some common types:
Centrifugal Pump
Magnetic Pump
Self-Priming Pump
Submersible Pump
Magnetic Drive Pumps: Utilize leak-free magnetic drive technology, suitable for transporting flammable, explosive, or toxic media (such as solvents, liquid chlorine).
Semi-Submersible Pumps: The motor is exposed above the liquid surface, suitable for applications with significant fluctuations in water level (such as drainage stations, temporary flood control).
Self-priming pumps: Equipped with an air release function, eliminating the need for manual priming, suitable for intermittent suction (e.g., ship ballasting, construction site drainage).
Diaphragm pumps: Utilize diaphragm reciprocating motion to transport high-viscosity or particulate-containing liquids (e.g., slurry, paint).
Water pumps: General-purpose design for clean water transportation (e.g., municipal water supply, agricultural irrigation).
Acid pumps: Manufactured using corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., PVDF, Hastelloy), specifically designed for acidic media (e.g., sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid).
Alkali pumps: Equipped with special seals and material processing techniques, suitable for strong alkaline liquids (e.g., sodium hydroxide, electrolyte).
What is centrifugal pump used for?
Industrial centrifugal pumps are widely used across multiple industries:
Water & Wastewater: Transferring clean water, sewage, and stormwater in treatment plants.
Oil & Gas: Transporting crude oil, refinery fluids, and seawater in offshore operations.
Chemical & Pharma: Handling corrosive acids, solvents, and sterile pharmaceutical liquids.
Power Plants: Circulating boiler feedwater, cooling water, and condensate in energy generation.
Mining & Manufacturing: Pumping abrasive slurries and industrial coolants.
Agriculture: Distributing irrigation water and agrochemicals efficiently.
Advantages of Centrifugal Pumps
High Efficiency: Engineered for optimal energy conversion, delivering superior flow rates with minimal power consumption.
Low Maintenance: Simplified mechanical design with only one rotating component (impeller) reduces wear and maintence.
Compact Footprint: Space-saving vertical/horizontal configurations adapt to constrained industrial layouts.
Material Versatility: Available in stainless steel, cast iron, fluoroplastic and advanced polymers to handle corrosive/abrasive media.
Pulsation-Free Operation: Continuous rotary motion ensures smooth, vibration-free fluid transfer critical for precision processes.
Conclusion
Centrifugal pumps are versatile, highly efficient, and widely used, making them the core equipment of modern fluid delivery systems. As a professional pump solution provider, we focus on meeting the special fluid handling needs of various industries and offer comprehensive customized services. If you need the most suitable pumping solution for your working conditions, please feel free to contact our technical experts for consultation.
Read More