Both magnetic drive pumps and centrifugal pumps belong to the category of centrifugal pumps, widely used in industrial fluid transfer applications. They both utilize centrifugal force to increase fluid kinetic energy and pressure, yet they exhibit numerous differences. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the differences between magnetic drive pumps vs centrifugal pumps. We'll comprehensively compare their working principles, structure, application areas, advantages, and disadvantages. This will help you clearly understand how to make the most informed choice based on your medium characteristics, safety requirements, and budget. Please continue reading to find the pumping solution best suited to your project needs.
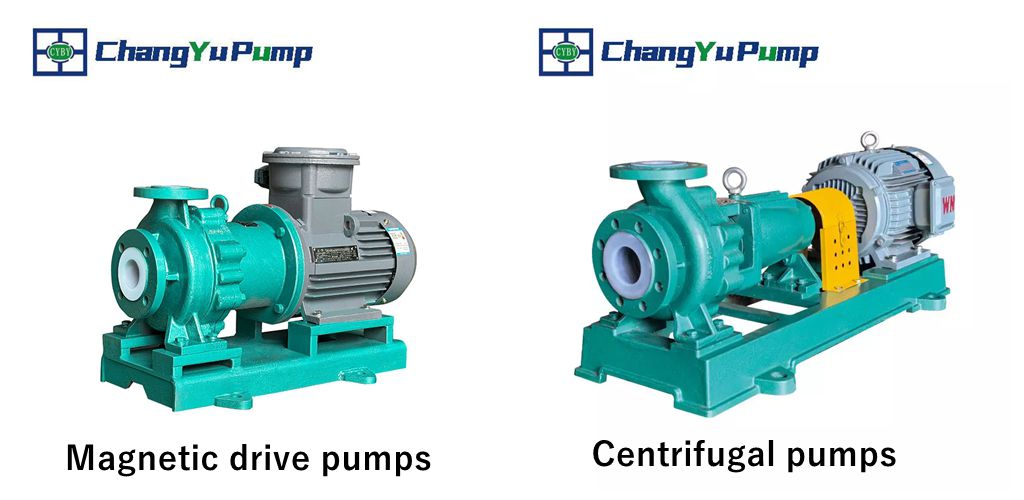
Magnetic Drive Pump: Magnetic drive pumps utilize magnetic coupling principles to transmit power. When the motor operates, it drives the outer magnetic rotor to rotate at high speed. Through the magnetic field interaction, the inner magnetic rotor within the isolation sleeve rotates synchronously, thereby driving the impeller to perform centrifugal motion. Its enclosed transmission structure fundamentally eliminates leakage risks. Although magnetic drive pumps employ a different transmission method, they still belong to the category of centrifugal pumps, all relying on the centrifugal force generated by impeller rotation to convey fluids.
Centrifugal Pump: As the most prevalent fluid transfer equipment, centrifugal pumps operate based on the centrifugal effect generated by impeller rotation. When the motor drives the pump shaft to rotate the impeller at high speed, the fluid is flung from the impeller's center toward its periphery under centrifugal force. During this process, the fluid's kinetic and pressure energy continuously increase, ultimately forming a stable flow stream discharged through the outlet. This highly efficient energy conversion method makes it the most widely used pump type in industrial applications.
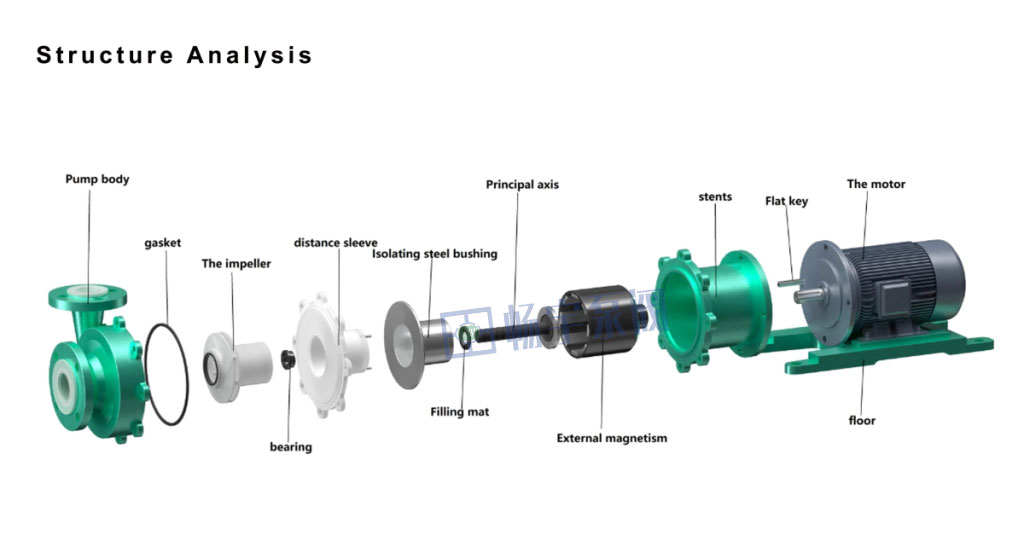
Magnetic drive pump: Magnetic pump mainly consists of two parts: the driving part (including the motor and the external magnet) and the transmission part (including the internal magnet and the impeller). The power transmission is achieved through magnetic coupling between the two parts, without the need for a traditional shaft seal structure, good sealing and leak-free.
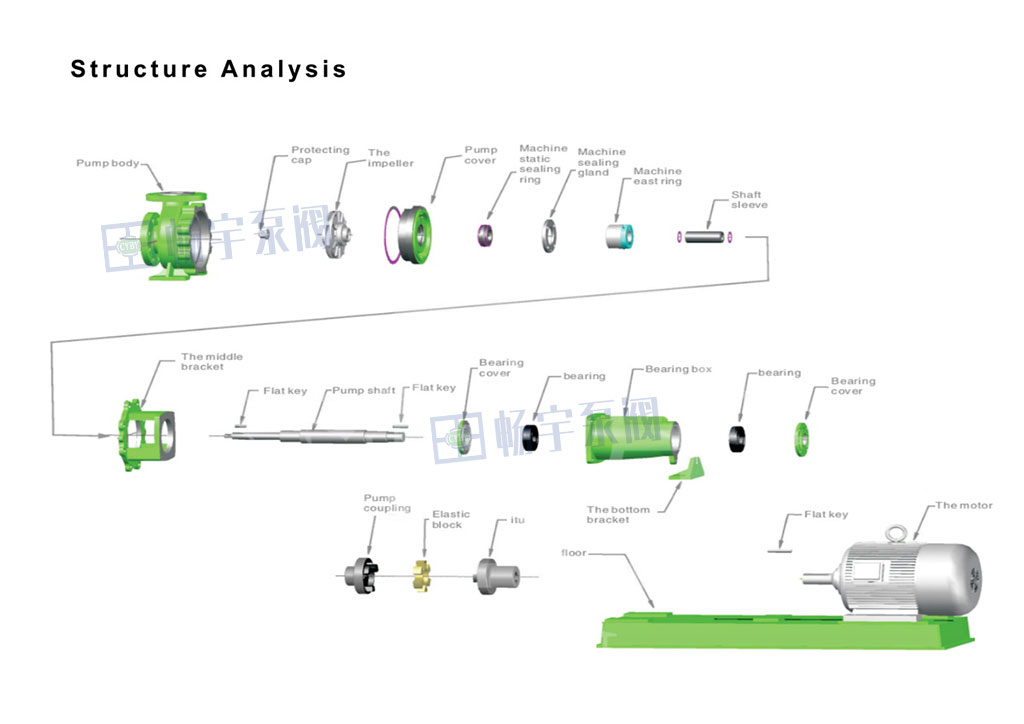
Centrifugal pump: Centrifugal pumps are usually composed of impellers, pump bodies, pump shafts, bearings, sealing rings and other parts. Among them, as an important component to block fluid leakage, the seal may fail due to wear or media corrosion during long-term operation, causing leakage problems.
Magnetic Drive Pumps: Featuring a shaftless design that completely eliminates leakage risks, magnetic drive pumps offer excellent corrosion resistance. They are particularly suitable for conveying flammable, explosive, toxic, or highly corrosive media. These pumps are widely used in high-risk and high-purity processes such as petroleum refining, fine chemicals, biopharmaceuticals, surface treatment, and environmental engineering.
Centrifugal Pumps: Centrifugal pumps feature robust mechanical construction, stable operational performance, and excellent adaptability to varying conditions, making them one of the most widely used fluid transfer devices. They are extensively applied in industrial processes, agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply and drainage, building fire protection, and HVAC systems.
Our hours
Mon 11/21 - Wed 11/23: 9 AM - 8 PM
Thu 11/24: closed - Happy Thanksgiving!
Fri 11/25: 8 AM - 10 PM
Sat 11/26 - Sun 11/27: 10 AM - 9 PM
(all hours are Eastern Time)