In the industrial and municipal sectors, pumps are essential components of fluid transport systems. Common pump types include sewage pumps and clean water pumps, which differ significantly in their structural design, application scenarios, and operating principles. Understanding the characteristics and usage of these two types of pumps will help companies make informed decisions regarding engineering design, equipment selection, and maintenance management.
This article will explain the definitions of sewage pumps and clean water pumps, how to choose the right pump, and the key differences in their structure and performance.
ChangYu Sewage pump is a drum pump, with a motor integrated into the pump. Compared to traditional horizontal or vertical sewage pumps, sewage pumps are compact and require less space. They are typically used to transport sewage containing solid particles or fibrous materials, industrial wastewater, and domestic wastewater. They are widely used in municipal wastewater treatment, industrial drainage, and low-lift drainage systems.
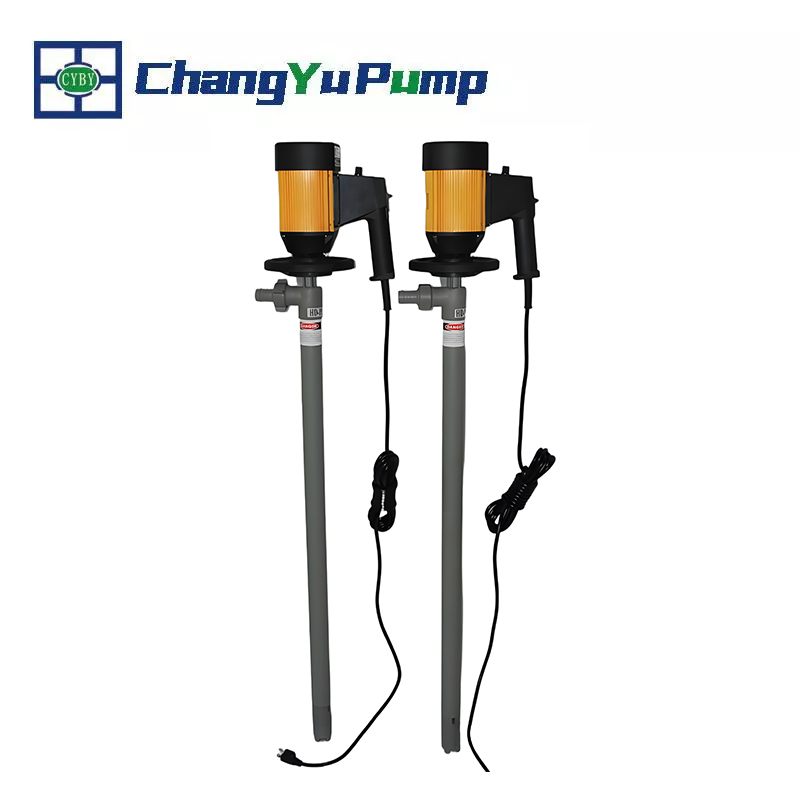

To prevent clogging, sewage pumps feature a large flow path design that allows for smooth passage of impurities and particles in the wastewater. However, due to this, their efficiency is slightly lower than that of clean water pumps, and their lift is generally not high.
Clean water pumps are primarily used to transport clean water or liquids with physical and chemical properties similar to clean water. They are widely used in industrial and municipal water supply and drainage, high-rise building pressure boosting, garden sprinkler irrigation, firefighting pressure boosting, long-distance transportation, HVAC/refrigeration cycles, farmland irrigation, and hot and cold water circulation systems.
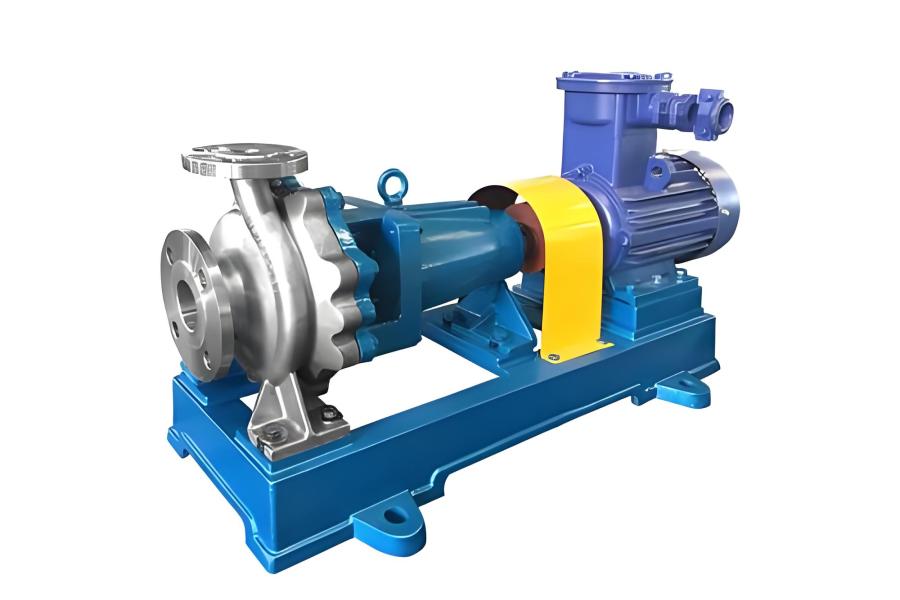
Clean water pumps are designed with smaller flow paths and tighter clearances, which allows them to achieve higher lift under the same conditions, making them suitable for high-pressure and long-distance transportation of clean water.
When selecting a pump, consider the liquid properties, conveying distance, required head, and on-site operating conditions:
Sewage pumps are suitable for:
Sewage, wastewater, industrial liquids containing solids
Low-head drainage, basement drainage, sewage treatment plants
Clean water pumps are suitable for:
Clean water or similar liquids
High-rise building water supply and boosting, fire protection systems, garden sprinkler irrigation, and hot and cold water circulation
Note: Due to the compact design of the flow path and impeller, clean water pumps are not suitable for sewage or liquids containing solids. If used for sewage, they are prone to clogging, entanglement, wear, or corrosion, resulting in damage or even failure of the pump.
This comparison shows that pump selection must be based on the liquid properties and operating environment. Failure to do so can lead to equipment damage, inefficiency, and even safety accidents.
In summary, sewage pumps and clean water pumps each have their advantages. The former is suitable for conveying sewage containing solids and industrial wastewater, while the latter is suitable for conveying and boosting clear water or similar liquids. In industrial, construction, and municipal engineering, choosing the right pump type is key to ensuring efficient and stable system operation. If you have any questions about sewage or clean water pump selection, application, or maintenance, or have specific purchasing needs, please feel free to contact our professional team for customized solutions and quotes.
Our hours
Mon 11/21 - Wed 11/23: 9 AM - 8 PM
Thu 11/24: closed - Happy Thanksgiving!
Fri 11/25: 8 AM - 10 PM
Sat 11/26 - Sun 11/27: 10 AM - 9 PM
(all hours are Eastern Time)